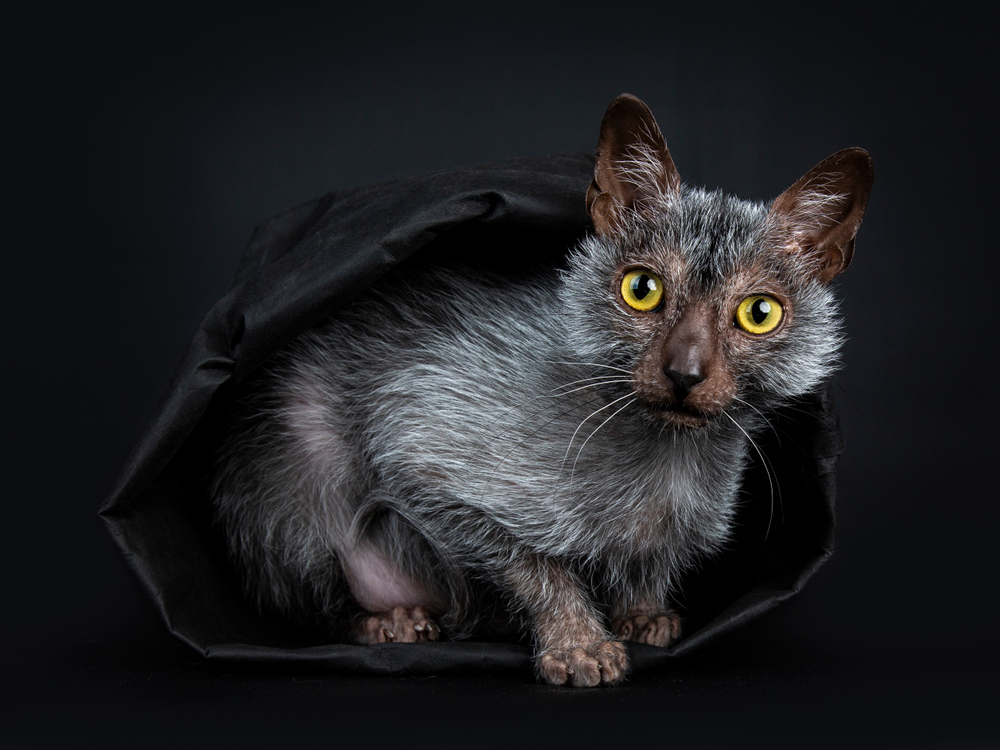
Scientists have unveiled a new species of archosaur, a reptile that existed around the dawn of the dinosaurs. The armored creature sported both crocodilian and dinosaur-like features, and roamed the planet more than 235 to 240 million years ago during the Triassic Period.
“We think [the creature lived] just before dinosaurs appear on the planet,” says Sterling Nesbitt, a paleobiologist at Virginia Tech and lead author on the new study.
What Are Archosaurs?
Archosaurs are a diverse group of creatures that can be traced all the way back to the Middle Triassic Period, which started roughly 246 million years ago. The group is divided roughly into two major branches: One of them evolved to include all living birds, non-bird dinosaurs and pterosaurs, while the other includes crocodilians.
Madagascar reptile reconstruction (Credit: © Nesbitt, et al./Zoological Journal of the Linnean Society)
There have been only about 15 specimens of creatures that predate dinos and crocodiles in the fossil record to date — most of them found in the past two decades. The recently described 235-million-year old specimen, Mambachiton fiandohana, was found in a deposit in southern Madagascar.
Read More: 99-Million-Year-Old Baby Bird Feathers Discovered From a Long-Extinct Species
How Was the New Species Found?
The first fossils of Mambachiton fiandohana were found in the late 1990s by John Flynn, a fossil curator at the American Museum of Natural History in New York. But it took a while for researchers to unearth all the fossils from that specimen, which include vertebrae, pelvis and scapula parts. That’s because the initial dig was focused more on ancient mammal fossils, so these archosaur fossils gathered academic dust for a time.
Nesbitt and his colleagues later determined that the various bones, though spread out over a great distance, seemed to be from the same individual based on the consistency in their size and the lack of duplication in the fossils. They published their results recently in a study in the Zoological Journal of the Linnean Society.
The creature would have been about the size of a golden retriever, says Nesbitt, but a little less heavy set. It was about three meters long from its snout to the base of its tail, and a little less than a foot would have separated its torso from the ground as it walked.
“It had characteristics more like a crocodile on stilts,” Nesbitt says, adding that they would have looked a little like the Teleocrater, another archosaur described a few years ago. “These are pretty lean animals.”
Read More: Human Ancestors Must Have Co-Existed With Dinosaurs, Study Says
Is the New Species of Archosaur a Dinosaur?
Unlike most early dinosaurs, the new study affirms that Mambachiton fiandohana had armored plates along its spine. Some later dinosaurs, like stegosaurus, eventually readapted this feature, though it’s more common in the crocodilian family.
The fossilized cervical vertebra — and overlaying osteoderms, which formed the plates of the newly-described species — of Mambachiton fiandohana. (Credit: © Nesbitt, et al./Zoological Journal of the Linnean Society)
Nonetheless, Nesbitt says that Mambachiton seems a little closer to dinosaurs and pterosaurs than crocodilians. While the creature sits close to both lineages, a few hallmarks — such as the pelvis — resemble those from dinosaurs and pterosaurs more closely than crocodilians, and the muscle scars on the femur also position the specimen closer to the dino side.
Nesbitt says that these small differences are what paleontologists expected to find, especially as researchers find fossils that sit closer to the common ancestor of all archosaurs. “The more information we get, we have to be more nuanced,” he says.
While researchers are indeed able to theorize (and reconstruct) what these creatures might have looked like, they can only confirm it when they discover fossils like Mambachiton.
Read More: How Do Scientists Reconstruct What Dinosaurs Looked Like?